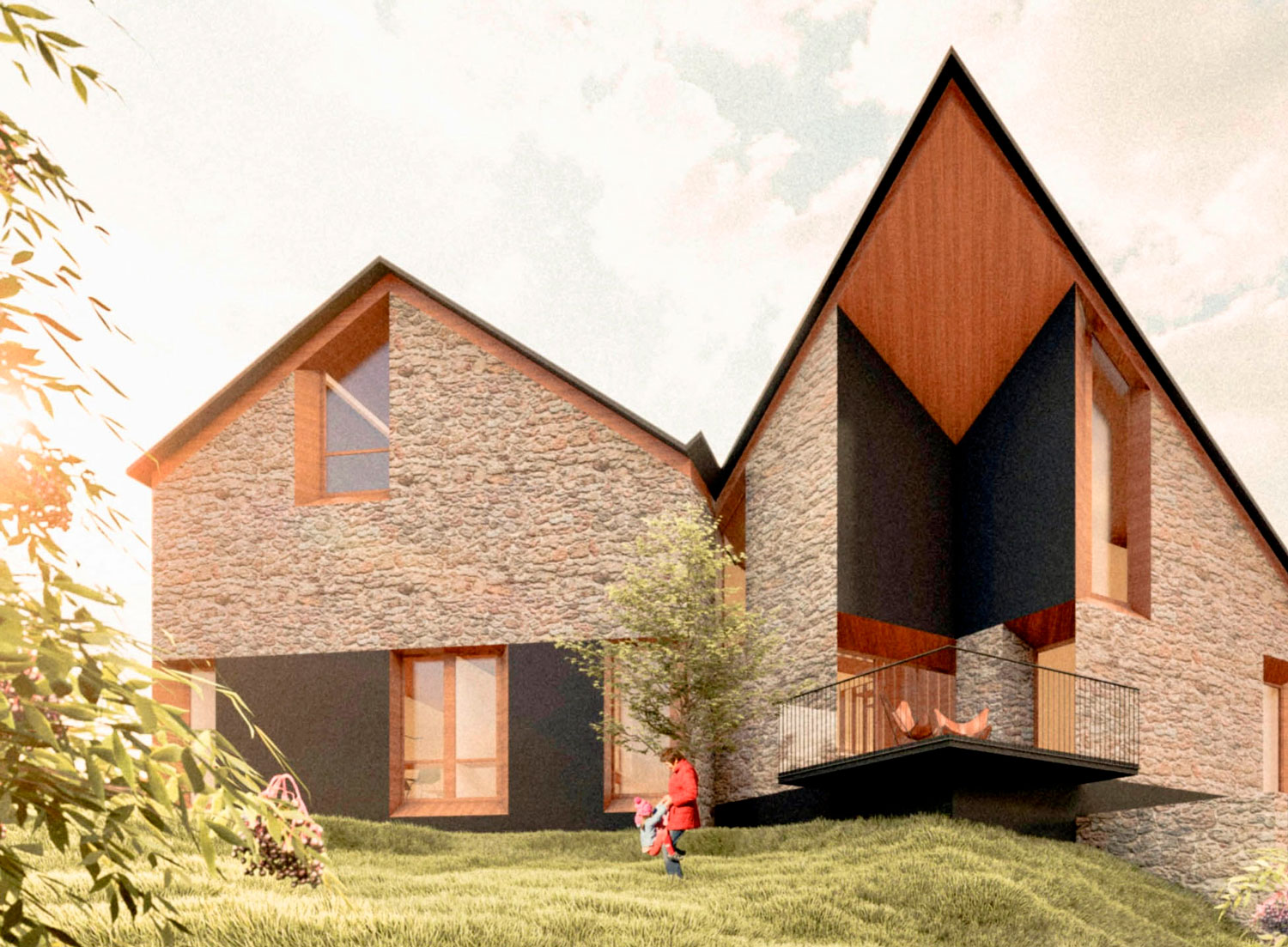
What is a Passive House?
A passive house, also known as a passivhaus or passive house, is a building designed to make the best use of available natural resources and minimize its environmental impact. This approach is based on a fundamental principle: “build better, consume less”. This construction standard means that passive houses are designed to be highly energy efficient, allowing the energy consumption for heating, cooling and ventilation to be extremely low. A passive house can reduce heating consumption by 90% compared to a traditional house.
The Fundamental Principles of a Passive House
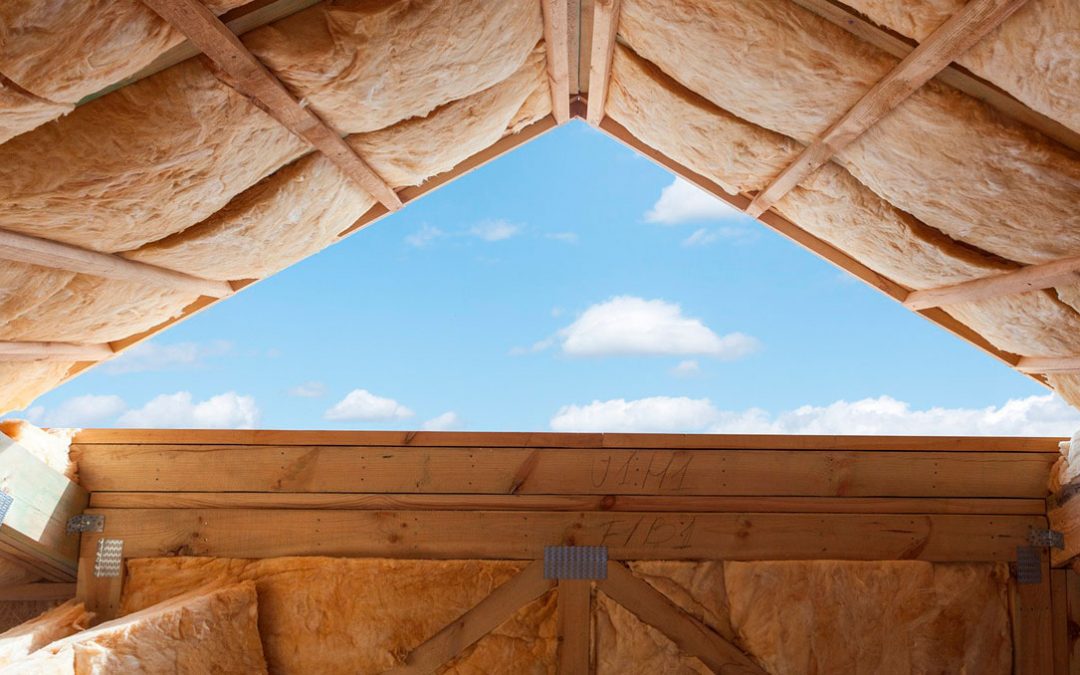
High-quality thermal insulation: Passive houses are designed with a highly insulated envelope, which prevents heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. This creates a comfortable and stable indoor environment all year round.
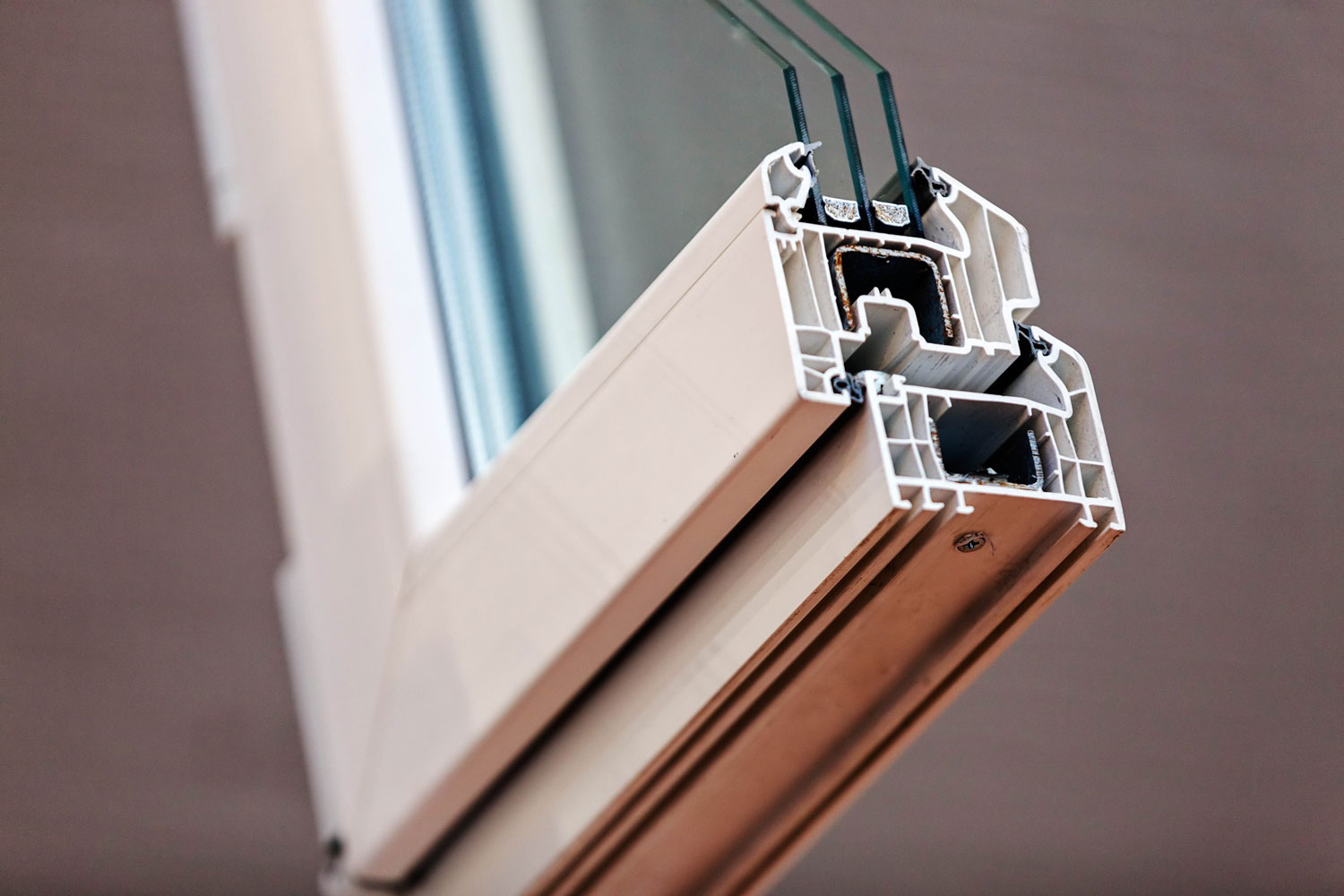
2. High efficiency windows: Windows are an essential component in a passive house, as they must be highly energy efficient and provide optimal thermal insulation.
3. Ventilation systems with heat recovery: A distinctive feature of passive houses is the controlled mechanical ventilation system with heat recovery. This allows fresh air to constantly enter while recovering heat from the indoor air, thus reducing the need for additional heating.
4. Absence of thermal bridges: To maintain maximum energy performance, passive houses must avoid thermal bridges, which are areas where heat is lost through poorly insulated connections between building elements.

Benefits of a passive house
1. Energy efficiency: Passive houses can significantly reduce energy consumption compared to conventional buildings, resulting in lower energy bills and a smaller carbon footprint.
2. Indoor comfort: Thanks to the high level of insulation and the ventilation system with heat recovery, passive houses offer a comfortable indoor environment, with balanced temperature and humidity in all seasons of the year.
3. Air quality: The controlled ventilation of a passive house ensures a constant supply of fresh, filtered air, which improves indoor air quality and promotes the health and well-being of its occupants.
4. Durability and long-term value: The high quality construction and materials used in the passive house result in durable buildings with high value over time.
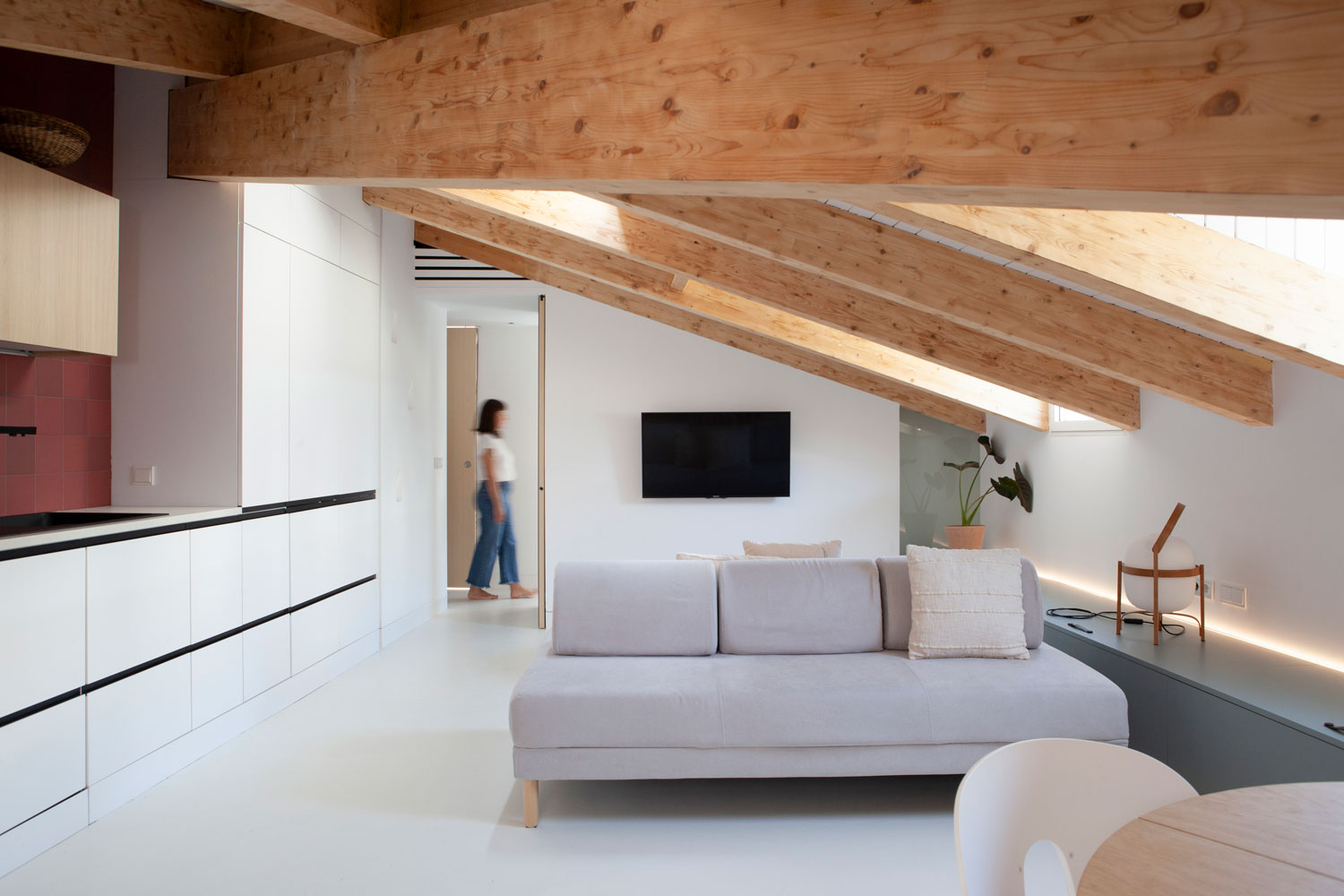

The Future of Sustainable Architecture
Passive houses are just one example of what can be achieved by combining architecture with sustainability. As awareness of climate change grows, it is critical that architects commit, as we do, to responsible design and energy efficiency in their projects.
In conclusion, passive houses are an inspiring example of how architecture can be a tool to take care of our planet and improve people’s quality of life. As architects, we have the power and responsibility to design a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future. Let’s continue to build with awareness and vision of the future!


