HEALTH AND ENERGY
In order to achieve complete thermal comfort and well-being inside buildings and modular homes, ventilation is a key factor, therefore mechanical ventilation is a great ally to prevent health problems, to achieve greater energy efficiency and adequate thermal comfort. Mechanical ventilation is a controlled active system that allows constant air renewal, thus ensuring indoor air quality, resulting in healthy environments. It ensures that the volume of extracted and supply air is the same, thus avoiding differences in pressure that may disturb people, as well as a uniform distribution of clean air, helps to reduce problems related to humidity and condensation, which prevents the formation of mold and fungi that can affect both the health of people and the structural integrity of the building. In addition, efficient ventilation reduces energy consumption by minimizing heat losses in winter and gains in summer.
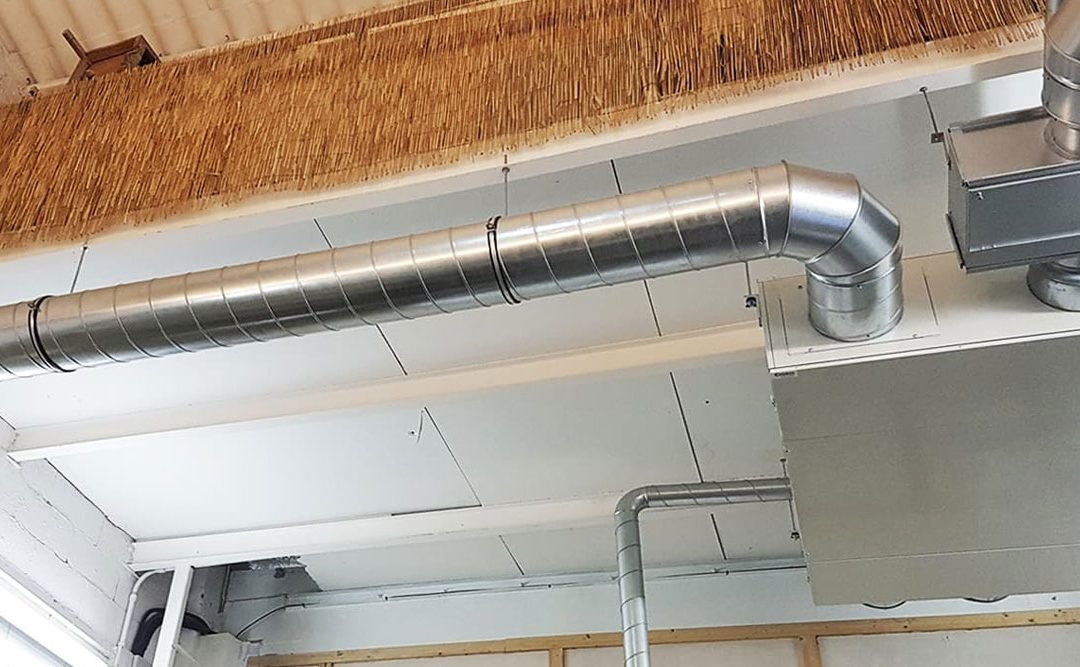
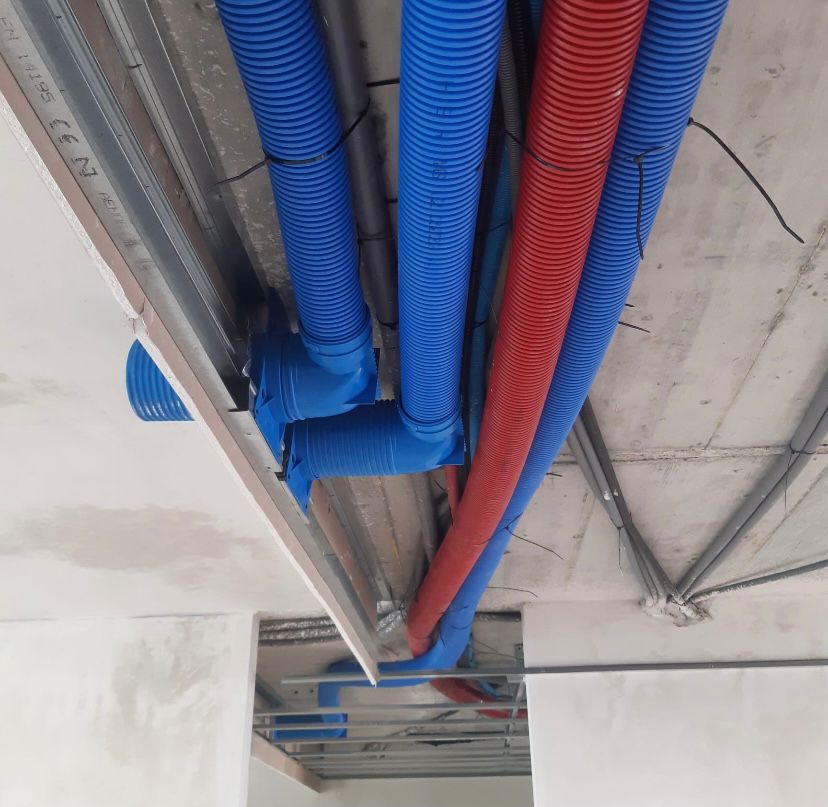
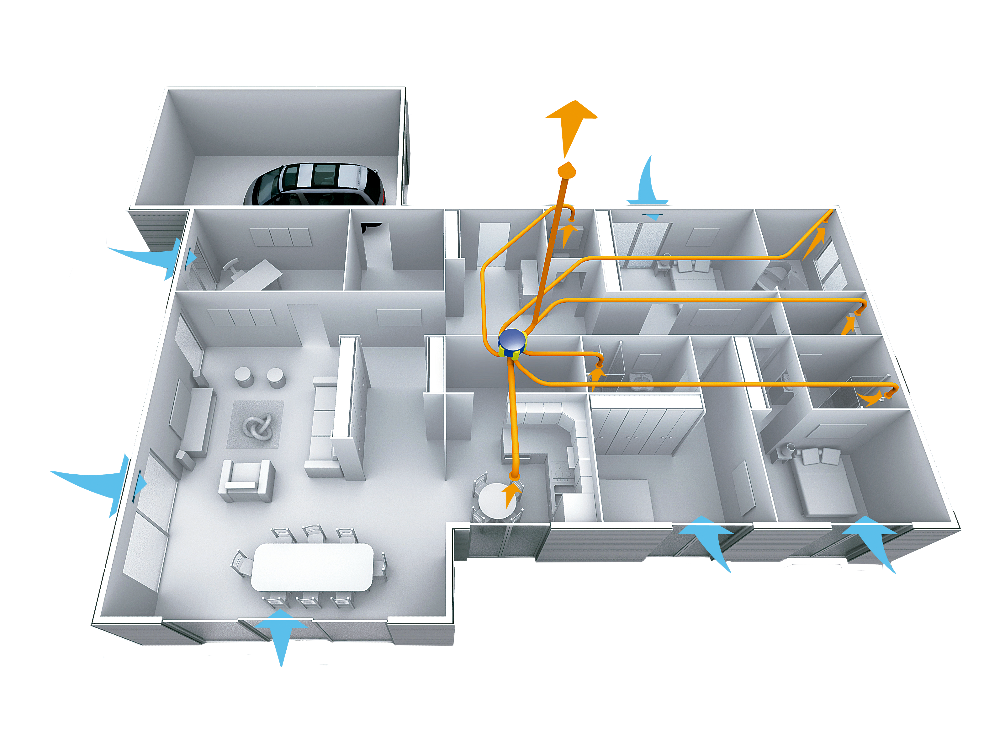
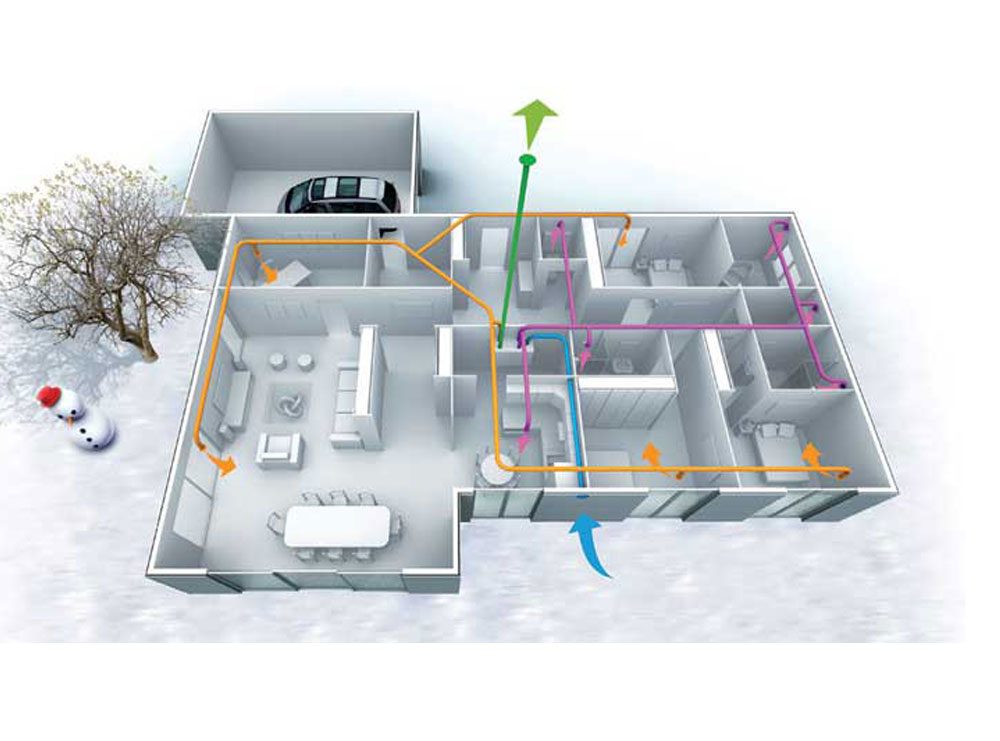
TYPES OF MECHANICAL VENTILATION FOR MODULAR HOUSING:
- Single-flow mechanical ventilation: stale air is extracted from the humid rooms, i.e. kitchen and bathrooms, and new air is introduced directly into the rest of the rooms, called dry rooms. It produces an imbalance in temperatures, it is the least efficient method.
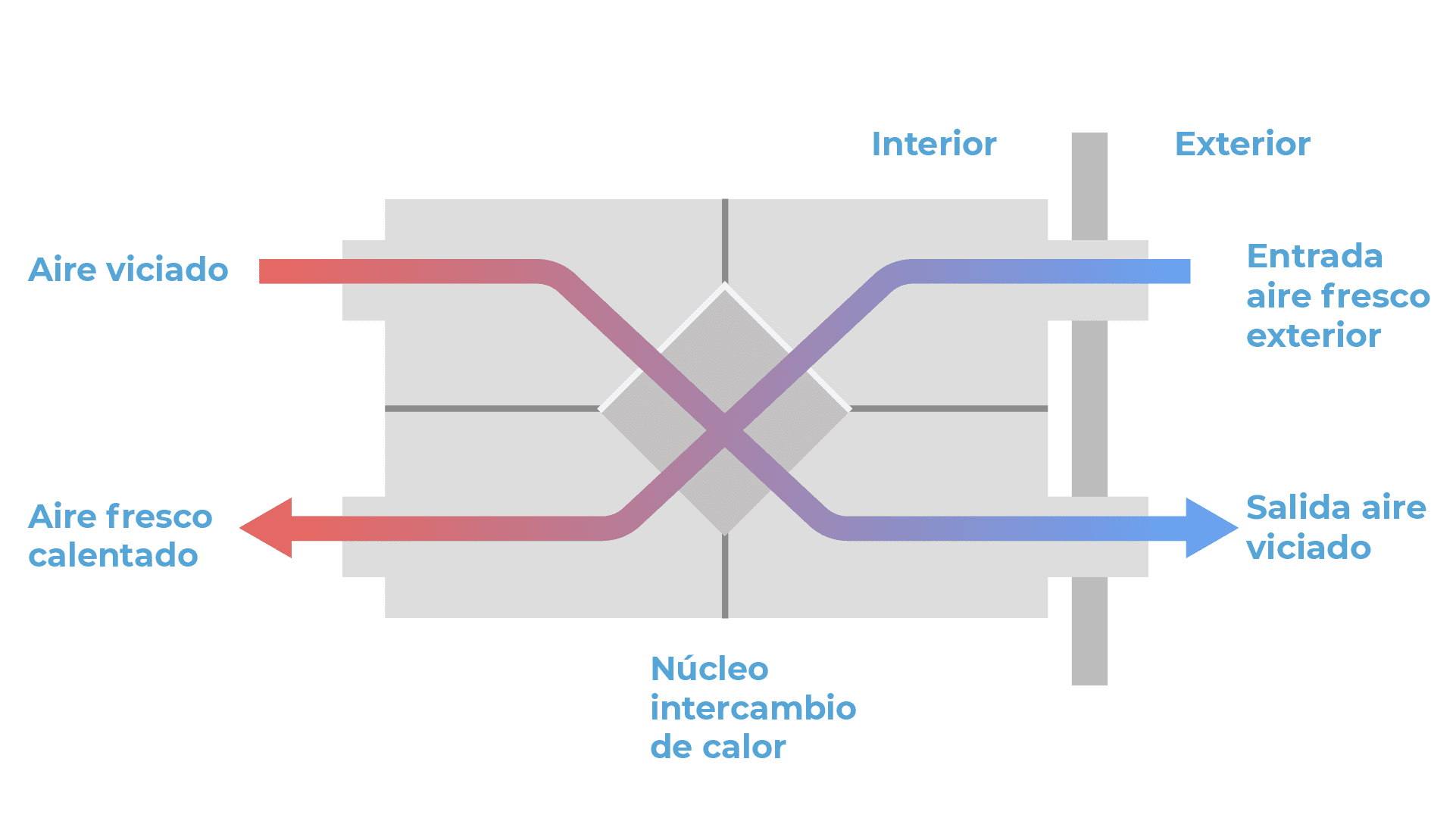
- Double flow mechanical ventilation: as in single flow, stale air is extracted from the humid rooms, but clean air is introduced into the dry rooms in a controlled manner. In addition, in this case there is the possibility of installing a heat recovery unit, these components allow to recover part of the energy of the extracted air, which is used to heat the new air and thus introduce it at a temperature similar to that of the interior. This fact, which saves energy, is perfect for integration into modular housing.
In our architectural studio Cronotopos, mechanical ventilation is a must in modular housing, as it is essential to create healthy, comfortable and sustainable living spaces.
In summary, the benefits of mechanical ventilation for modular housing are:
- Indoor Air Quality Control: removal of pollutants, such as dust, smoke and odors and filters the air by removing fine particles and allergens.
- Humidity regulation: maintains adequate humidity levels, preventing problems such as mold and mildew.
- Energy efficiency: minimizes energy loss compared to uncontrolled natural ventilation.
- Thermal comfort: controlled temperature creates comfortable environments throughout the year.
- Improved well-being: reducing respiratory diseases and allergies, as well as generating more productive spaces, thanks to air quality and thermal comfort.
- Design flexibility: they adapt to the requirements of the building.
- Sustainability: reduces carbon footprint and can help to obtain environmental certificates.
Written by Paula del Río, published by Cronotopos.


